Limit equilibrium slope stability analysis using Slide2 and Slide3
Online course |
|
50 hours / 6 weeks |
|
|
Dates: 1st of July to 12th of August |
| Standard | Unemployed Or Student |
| $421 | $313 |
Full-featured versions of Slide2 and Slide3 software included
Introduction
This course is aimed for students with a geotechnical, mining or civil engineering background and interested to have certified professional training in the Limit Equilibrium Method, with a focus on Slope Stability in grounds or rockmasses (where its behavior is adequate for LEM modelling). The goal of this course is to give the students a brief understanding of the Limit Equilibrium Method and to provide the necessary knowledge using one of the most advanced LEM software from Rocscience – Slide2D and 3D, which can then be applied directly in consulting companies, scientific research institutes/ universities and any other design & build mining/ civil engineering contractors.
With this objective in mind, the course is completely structured into software applications and practical subjects that include Rocscience’s professional software currently used on the global market.
The main pre-requisite for this course would be undergraduate and/ or post-graduate courses in Rock Mechanics, Soil Mechanics and/ or Computational Geomechanics. An introductory Slope Stability Analysis using Limit Equilibrium Method course would be highly recommended, but this is not mandatory, as a summary of the methodology will be presented within the course.
Objectives
The objectives of this course are to consolidate the foundations of the Limit Equilibrium Method, by thinking mainly about its application in geotechnical, mining and civil engineering slope stability analysis, although the basic ideas can be generalized without any difficulty. Furthermore, it should be noted that the subject starts with the most basic concepts, initially treated intuitively in order to allow them to be easily assimilated by the students without any knowledge in slope stability analysis.
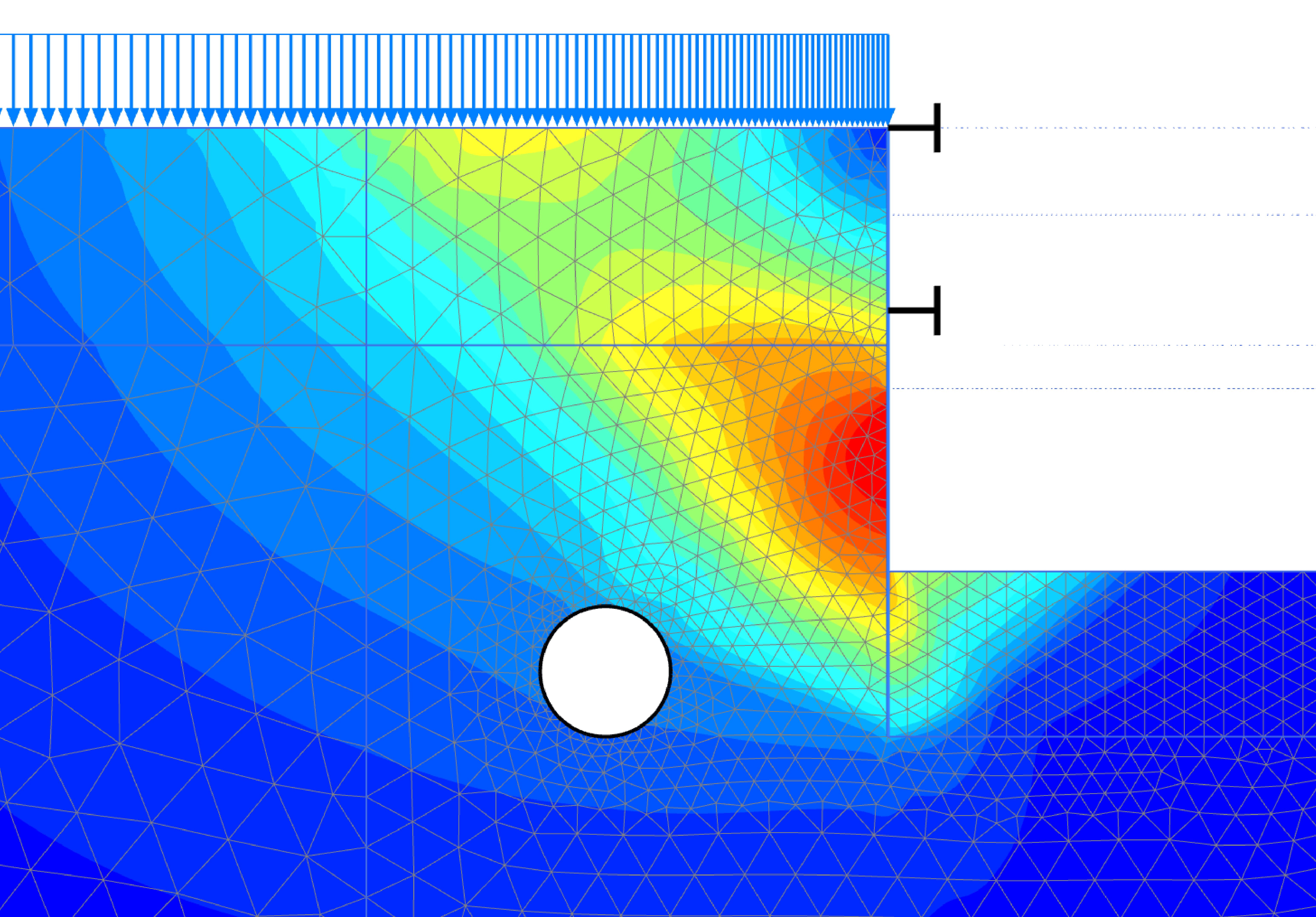
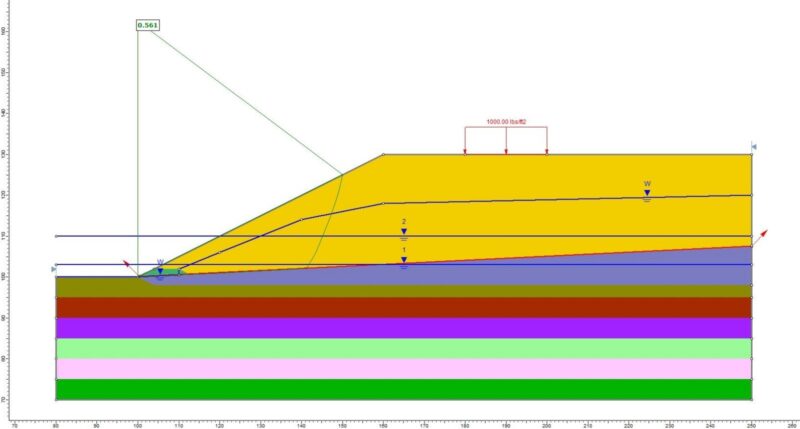
This course provides 2D and 3D soil & rock mechanics stability solutions for slopes, dams, embankments, levees, using any combination of constitutive models for materials and various types of support: rockbolts/ soil nails, anchorages/ grouted tiebacks, piles/ micro piles, geosynthetics, and any other user defined support. Analysis are carried out in drained and undrained conditions, taking into account groundwater influence on slope stability. Basic knowledge on statistics and probabilistic design are presented, as well as standard design codes (EC7).
Limited places.
- Module I – Basics of Limit Equilibrium Methods for Slope Stability Analysis
-
- – 1.1 Objectives of slope stability analysis
- – 1.2 Stability of rotational and translational failure mechanisms
- – 1.3 Geotechnical factors affecting slope stability and failure
- 1.4 Design acceptance criteria
- – 1.4.1 Safety Factors
- – 1.4.2 Risk based design
- – Probability of Failure (PF)
- – Reliability Index (RI)
- – 1.4.3 Reference to EC7 Design Codes
- – 1.5 Limit Equilibrium – Slope Stability Analysis Methods in Slide2 & 3 – a Review: Bishop, Janbu, Morgenstern… Sarma Non-vertical slices
- – 1.6 Project 1 – Slope Stability Analysis using LEM (hand calculations)
- Module II – Overview of Slide2
- – 2.1 Modeler – Geometry, boundary conditions, loading
- – 2.2 Engine
- – 2.3 Interpreter
- – 2.4 Project 2 – Geometry: Developing model geometries in 2D
- Module III – Slope Stability Analysis with Slide2
- – 3.1 Material constitutive models
- – 3.2 Anisotropic material strength models and Weak layers
- – 3.3 Geometry search options and optimization techniques
- – 3.4 Soil profile & Multi-Scenario modelling
- – 3.5 Support systems for slopes
- – 3.6 Interpretation of Slide2 models
- – 3.7 Project 3 – Individual case study (comparison with Project 1)
- Module IV – Groundwater Modelling with Slide2
- – 4.1 Phreatic lines and Excess pore water pressure
- – 4.2 Boundary conditions & Permeability functions
- – 4.3 Saturated – unsaturated steady – state groundwater analysis
- – 4.4 Transient groundwater modelling
- – 4.5 Seepage analysis and effect on Safety Factor
- – 4.6 Rapid drawdown
- – 4.7 Project 4 – Groundwater modelling
- 3D Limit Equilibrium Analysis with Slide3
- – 5.1 Overview of Limit Equilibrium Slope Stability Analysis using Slide3
- – Modeler
- – Compute
- – Interpreter
- – 5.2 Building 3D models from primitives, Slope wizard and Import geometry
- – 5.3 Surface reconstruction from contour maps, point clouds and boreholes
- – 5.4 Slip surfaces overview and Search algorithms
- – 5.5 Support design
- – 5.6 Interpretation of Slide3 models
- – 5.7 Project 5 – Slide3 case study
- – 5.1 Overview of Limit Equilibrium Slope Stability Analysis using Slide3
- Continuous assessment exercises review
- Evaluation and grading
Dr. Gelu Madear
Dr. Gelu MADEAR graduated from the most prestigious Mining Institute in Southeastern Europe, (today called the University of Petrosani, Romania) with a B.Sc. in Mining Engineering in 1990. He also received an M.Sc. in Environmental Engineering from Polytechnic University of Turin, Italy, followed by a Ph.D. in Mining Engineering from the University of Petrosani, Transylvania, Romania.
Dr. Gelu MADEAR had held long term faculty appointments as Lecturer at the University of Petrosani, Romania, where he was also Director of the M.Sc. Course in EIA – Environmental Impact Assessment and Professor/ Director Geomechanics of the Polytechnic of Namibia, Windhoek.
For more than 10 years he worked in the consultancy sector in the UK and currently is an Independent International Consultant in Computational Geomechanics.
Dr. Gelu MADEAR has over 30 years’ experience in Civil, Mining & Environmental Engineering including academic, design and consulting, with expertise in geomechanical and geotechnical design, including numerical methods and probabilistic approaches of underground structures, in various ground conditions – from jointed rock masses to frozen grounds; used various rock mechanics and geotechnical software packages, inclusive of ITASCA – FLAC2D/ 3D, UDEC, PLAXIS 2D/ 3D, ROCSCIENCE – SLIDE 2 & 3, DIPS, SWEDGE, UNWEDGE, RocFall, RocPlane, RocTopple, RSData, RSPile, RocSupport, RS2, RS3, Examine2D, Examine3D, CivilFEM, SALOME MECA/ CODE ASTER. Implementation of Discrete Fracture Networks in Computational Geomechanics (FLAC3D) using FracMan, especially in Block Cave Mining.
He has excellent interpersonal and communications skills with the ability to work with a team from diverse disciplines, companies and nationalities.
The course is delivered online through our easy-to-use Virtual Campus platform. For this course, a variety of content is provided including:
– eLearning materials
– Videos
– Interactive multimedia content
– Live webinar classes
– Texts and technical articles
– Case studies
– Assignments and evaluation exercises
Students can download the materials and work through the course at their own pace.
We regularly update this course to ensure the latest news and state-of-the-art developments are covered, and your knowledge of the subject is current.
Live webinars form part of our course delivery. These allow students and tutors to go through the course materials, exchange ideas and knowledge, and solve problems together in a virtual classroom setting. Students can also make use of the platform’s forum, a meeting point to interact with tutors and other students.
The tutoring system is managed by email. Students can email the tutor with any questions about the course and the tutor will be happy to help.
The course is aimed at engineers at all levels and students in the last academic year, working or studying in civil and mining engineering areas, especially in the geotechnical field – consulting engineering companies, universities, research & development companies, civil & mining engineering contractors.
Fundamentals of Limit Equilibrium Slope Stability Analysis using Slide2 & 3 will teach students how to start working in Slide2 & 3 by Rocscience. They will learn how to perform basic slope stability analysis using the standard Graphic User Interface and program approach. The course was created to provide a powerful tool to assist civil & geotechnical/ mining engineers with any type of slope stability problem. Some previous experience in using similar programs would be desirable, although it is not a pre-requisite.
The course contains detailed hands-on examples very useful for those interested in learning about Creating Geometry, Material & Sections, Loads & Boundary Conditions, Support and Groundwater steady-state and transient analysis and introduction to metaheuristic types of searches for failure surfaces.
Once a student finishes the course and successfully completes the assignments and evaluation tests, they are sent an accreditation certificate. The certificate is issued by Ingeoexpert to verify that the student has passed the course. It is a digital certificate that is unique and tamper-proof – it is protected by Blockchain technology. This means it is possible for anyone to check that it is an authentic, original document.
You will be able to download the certificate in an electronic format from the Virtual Campus platform. The certificate can be forwarded by email, shared on social networks, and embedded on websites. To see an example, click here.
Job prospects for this course would be mainly civil, mining and geotechnical engineers, especially in the geotechnical field – working on consulting engineering companies, universities, research & development companies, civil & mining engineering contractors.
Full-featured versions of Slide2 and Slide3 software included
Introduction
This course is aimed for students with a geotechnical, mining or civil engineering background and interested to have certified professional training in the Limit Equilibrium Method, with a focus on Slope Stability in grounds or rockmasses (where its behavior is adequate for LEM modelling). The goal of this course is to give the students a brief understanding of the Limit Equilibrium Method and to provide the necessary knowledge using one of the most advanced LEM software from Rocscience – Slide2D and 3D, which can then be applied directly in consulting companies, scientific research institutes/ universities and any other design & build mining/ civil engineering contractors.
With this objective in mind, the course is completely structured into software applications and practical subjects that include Rocscience’s professional software currently used on the global market.
The main pre-requisite for this course would be undergraduate and/ or post-graduate courses in Rock Mechanics, Soil Mechanics and/ or Computational Geomechanics. An introductory Slope Stability Analysis using Limit Equilibrium Method course would be highly recommended, but this is not mandatory, as a summary of the methodology will be presented within the course.
Objectives
The objectives of this course are to consolidate the foundations of the Limit Equilibrium Method, by thinking mainly about its application in geotechnical, mining and civil engineering slope stability analysis, although the basic ideas can be generalized without any difficulty. Furthermore, it should be noted that the subject starts with the most basic concepts, initially treated intuitively in order to allow them to be easily assimilated by the students without any knowledge in slope stability analysis.
This course provides 2D and 3D soil & rock mechanics stability solutions for slopes, dams, embankments, levees, using any combination of constitutive models for materials and various types of support: rockbolts/ soil nails, anchorages/ grouted tiebacks, piles/ micro piles, geosynthetics, and any other user defined support. Analysis are carried out in drained and undrained conditions, taking into account groundwater influence on slope stability. Basic knowledge on statistics and probabilistic design are presented, as well as standard design codes (EC7).
Limited places.
- Module I – Basics of Limit Equilibrium Methods for Slope Stability Analysis
-
- – 1.1 Objectives of slope stability analysis
- – 1.2 Stability of rotational and translational failure mechanisms
- – 1.3 Geotechnical factors affecting slope stability and failure
- 1.4 Design acceptance criteria
- – 1.4.1 Safety Factors
- – 1.4.2 Risk based design
- – Probability of Failure (PF)
- – Reliability Index (RI)
- – 1.4.3 Reference to EC7 Design Codes
- – 1.5 Limit Equilibrium – Slope Stability Analysis Methods in Slide2 & 3 – a Review: Bishop, Janbu, Morgenstern… Sarma Non-vertical slices
- – 1.6 Project 1 – Slope Stability Analysis using LEM (hand calculations)
- Module II – Overview of Slide2
- – 2.1 Modeler – Geometry, boundary conditions, loading
- – 2.2 Engine
- – 2.3 Interpreter
- – 2.4 Project 2 – Geometry: Developing model geometries in 2D
- Module III – Slope Stability Analysis with Slide2
- – 3.1 Material constitutive models
- – 3.2 Anisotropic material strength models and Weak layers
- – 3.3 Geometry search options and optimization techniques
- – 3.4 Soil profile & Multi-Scenario modelling
- – 3.5 Support systems for slopes
- – 3.6 Interpretation of Slide2 models
- – 3.7 Project 3 – Individual case study (comparison with Project 1)
- Module IV – Groundwater Modelling with Slide2
- – 4.1 Phreatic lines and Excess pore water pressure
- – 4.2 Boundary conditions & Permeability functions
- – 4.3 Saturated – unsaturated steady – state groundwater analysis
- – 4.4 Transient groundwater modelling
- – 4.5 Seepage analysis and effect on Safety Factor
- – 4.6 Rapid drawdown
- – 4.7 Project 4 – Groundwater modelling
- 3D Limit Equilibrium Analysis with Slide3
- – 5.1 Overview of Limit Equilibrium Slope Stability Analysis using Slide3
- – Modeler
- – Compute
- – Interpreter
- – 5.2 Building 3D models from primitives, Slope wizard and Import geometry
- – 5.3 Surface reconstruction from contour maps, point clouds and boreholes
- – 5.4 Slip surfaces overview and Search algorithms
- – 5.5 Support design
- – 5.6 Interpretation of Slide3 models
- – 5.7 Project 5 – Slide3 case study
- – 5.1 Overview of Limit Equilibrium Slope Stability Analysis using Slide3
- Continuous assessment exercises review
- Evaluation and grading
Dr. Gelu Madear
Dr. Gelu MADEAR graduated from the most prestigious Mining Institute in Southeastern Europe, (today called the University of Petrosani, Romania) with a B.Sc. in Mining Engineering in 1990. He also received an M.Sc. in Environmental Engineering from Polytechnic University of Turin, Italy, followed by a Ph.D. in Mining Engineering from the University of Petrosani, Transylvania, Romania.
Dr. Gelu MADEAR had held long term faculty appointments as Lecturer at the University of Petrosani, Romania, where he was also Director of the M.Sc. Course in EIA – Environmental Impact Assessment and Professor/ Director Geomechanics of the Polytechnic of Namibia, Windhoek.
For more than 10 years he worked in the consultancy sector in the UK and currently is an Independent International Consultant in Computational Geomechanics.
Dr. Gelu MADEAR has over 30 years’ experience in Civil, Mining & Environmental Engineering including academic, design and consulting, with expertise in geomechanical and geotechnical design, including numerical methods and probabilistic approaches of underground structures, in various ground conditions – from jointed rock masses to frozen grounds; used various rock mechanics and geotechnical software packages, inclusive of ITASCA – FLAC2D/ 3D, UDEC, PLAXIS 2D/ 3D, ROCSCIENCE – SLIDE 2 & 3, DIPS, SWEDGE, UNWEDGE, RocFall, RocPlane, RocTopple, RSData, RSPile, RocSupport, RS2, RS3, Examine2D, Examine3D, CivilFEM, SALOME MECA/ CODE ASTER. Implementation of Discrete Fracture Networks in Computational Geomechanics (FLAC3D) using FracMan, especially in Block Cave Mining.
He has excellent interpersonal and communications skills with the ability to work with a team from diverse disciplines, companies and nationalities.
The course is delivered online through our easy-to-use Virtual Campus platform. For this course, a variety of content is provided including:
– eLearning materials
– Videos
– Interactive multimedia content
– Live webinar classes
– Texts and technical articles
– Case studies
– Assignments and evaluation exercises
Students can download the materials and work through the course at their own pace.
We regularly update this course to ensure the latest news and state-of-the-art developments are covered, and your knowledge of the subject is current.
Live webinars form part of our course delivery. These allow students and tutors to go through the course materials, exchange ideas and knowledge, and solve problems together in a virtual classroom setting. Students can also make use of the platform’s forum, a meeting point to interact with tutors and other students.
The tutoring system is managed by email. Students can email the tutor with any questions about the course and the tutor will be happy to help.
The course is aimed at engineers at all levels and students in the last academic year, working or studying in civil and mining engineering areas, especially in the geotechnical field – consulting engineering companies, universities, research & development companies, civil & mining engineering contractors.
Fundamentals of Limit Equilibrium Slope Stability Analysis using Slide2 & 3 will teach students how to start working in Slide2 & 3 by Rocscience. They will learn how to perform basic slope stability analysis using the standard Graphic User Interface and program approach. The course was created to provide a powerful tool to assist civil & geotechnical/ mining engineers with any type of slope stability problem. Some previous experience in using similar programs would be desirable, although it is not a pre-requisite.
The course contains detailed hands-on examples very useful for those interested in learning about Creating Geometry, Material & Sections, Loads & Boundary Conditions, Support and Groundwater steady-state and transient analysis and introduction to metaheuristic types of searches for failure surfaces.
Once a student finishes the course and successfully completes the assignments and evaluation tests, they are sent an accreditation certificate. The certificate is issued by Ingeoexpert to verify that the student has passed the course. It is a digital certificate that is unique and tamper-proof – it is protected by Blockchain technology. This means it is possible for anyone to check that it is an authentic, original document.
You will be able to download the certificate in an electronic format from the Virtual Campus platform. The certificate can be forwarded by email, shared on social networks, and embedded on websites. To see an example, click here.
Job prospects for this course would be mainly civil, mining and geotechnical engineers, especially in the geotechnical field – working on consulting engineering companies, universities, research & development companies, civil & mining engineering contractors.
1 review for Limit equilibrium slope stability analysis using Slide2 and Slide3
More info
Finish this course and get a certificate based on Blockchain
Limit equilibrium slope stability analysis using Slide2 and Slide3

Blockchain technology makes the certificate incorruptible, enabling companies to verifiy its autenticity.
Limit equilibrium slope stability analysis using Slide2 and Slide3
| $421 | $313 | |
| Get more information |



Horacio Diaz –
Good effort from the teacher to let us learn the basics of slope global equilibrium.